Difference between revisions of "SQL Browser"
From AgileApps Support Wiki
imported>Aeric |
imported>Aeric |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
:[[File:SQLBrowserSelect.png]] | :[[File:SQLBrowserSelect.png]] | ||
How it works: | ;How it works: | ||
:* The navigation pane on the left shows all of the tables in your database. | :* The navigation pane on the left shows all of the tables in your database. | ||
:* Clicking the arrow next to one expands the tree, showing the columns in the table | :* Clicking the arrow next to one expands the tree, showing the columns in the table | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
:: [[File:SQLBrowserGoButton.png]] | :: [[File:SQLBrowserGoButton.png]] | ||
''Learn more: | ;Considerations: | ||
:* Syntax is not case-sensitive, except for table names. | |||
:* If the table name is one of the [[SQL Reserved Words]], then it must be enclosed in back-ticks (<tt>`</tt>). | |||
: For example, "Order" is a reserved word in SQL (it's part of the "ORDER BY" clause), so a query on a table named "Order" will look like this: <tt>SELECT * FROM `ORDER`</tt>. | |||
: Without the backticks, you get an error like this: | |||
::<tt>Encountered "Order" at line 1, column 15. Was expecting (...</tt> | |||
::which means that parser found a word it recognized, but didn't find the things it expected to see before it got to that word. | |||
;Learn more: | |||
:* [[SQL Syntax]] | :* [[SQL Syntax]] | ||
:* [[SQL Functions]] | :* [[SQL Functions]] | ||
Revision as of 00:06, 11 November 2011
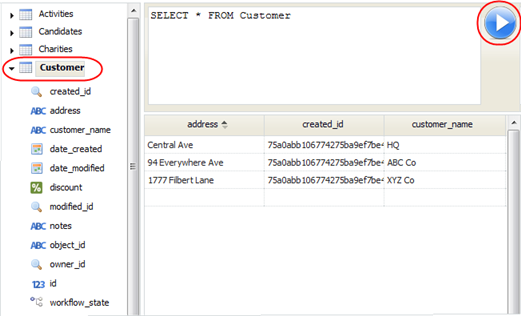
Designer > Data > Objects > [SQL Browser]
The SQL Browser gives you a graphical interface that lets you enter a SQL query and view the results:
- How it works
-
- The navigation pane on the left shows all of the tables in your database.
- Clicking the arrow next to one expands the tree, showing the columns in the table
- Double-clicking a table populates the statement pane with a default query (SELECT *) from that table.
- Clicking the triangle-button on the right runs the query.
- Considerations
-
- Syntax is not case-sensitive, except for table names.
- If the table name is one of the SQL Reserved Words, then it must be enclosed in back-ticks (`).
- For example, "Order" is a reserved word in SQL (it's part of the "ORDER BY" clause), so a query on a table named "Order" will look like this: SELECT * FROM `ORDER`.
- Without the backticks, you get an error like this:
- Encountered "Order" at line 1, column 15. Was expecting (...
- which means that parser found a word it recognized, but didn't find the things it expected to see before it got to that word.
- Learn more