Scheduled Rules
![]() > Case Automation > Business Rules > Scheduled Rules
> Case Automation > Business Rules > Scheduled Rules
![]() > Objects > {object} > Business Rules > Scheduled Rules
> Objects > {object} > Business Rules > Scheduled Rules
Scheduled Rules let you carry out a series of actions on specific dates and times. They can be set up to repeat. For example, you can create one that runs once a month to assign all recent cases with a dissatisfied customer to a Review team.
To create or modify a Scheduled Rule:
- Go to
 > Case Automation > Business Rules > Scheduled Rules
> Case Automation > Business Rules > Scheduled Rules
or > Objects > {object} > Business Rules > Scheduled Rules
> Objects > {object} > Business Rules > Scheduled Rules - Select an existing rule, or click [New Rule]
- Fill in the information below
- Click [Save]
Basic Information
- Name - Give the timer event a name.
- Activation Date and Time- Designate the date and time at which the Rule is in force.
- Repeating Frequency - Choose how often to repeat the rule: Daily, Weekly, Monthly, or Yearly.
- Learn more: Repeating Frequency
Execution Criteria
Note: Scheduled Rules do not have an option to run unconditionally. Without a condition, a Scheduled Rule operates on every record, which can become computationally expensive. Also, a scheduled rule executes based on the Time Zone set under Account Management > Company Information > Locale Information and does not follow the system time.
Actions to Perform
- Selecting actions
- Select the action to perform when Rule conditions are satisfied.
(Possible actions are listed below) - As with conditions, additional options appear, depending on the action you select.
- Click [Add More] to specify additional actions.
- Available Actions
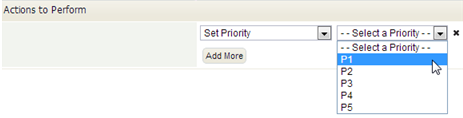
Set Priority
- This option appears for Cases. It allows the priority to be changed--for example from "P2" to "P1"
- Trigger Rules - This option enables the firing of Case-update rules.
Set Status
- This option appears for Cases. It allows the status to be changed--for example, to Closed
- Trigger Rules - This option enables the firing of Case-update rules.
Add Record
- Select an object to add a record to, and specify field values for the record:
- Do Not Trigger Rules - By default, Rules are enabled when adding a record. This option disables them.
- Use the Field Chooser to select object fields.
- For each field, use the Formula Builder to specify the field value.
Update Record
- Modify data in the current record
- Trigger Rules - This option enables the firing of record-updated rules.
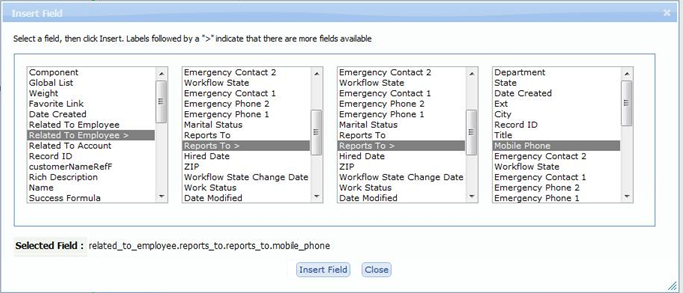
- Use the Field Chooser to select fields to modify -- including fields in a record targeted by a Lookup field in the current record, or fields targeted by Lookups in those records, and so on, as shown here:
- For each field, use the Formula Builder to specify the field value.
Add Note
- Add a note to the current record.
- Enter text for the note in the text area
- Use the field selector to add record variables
- Example: This note is for $user.full_name.
Assign to User
- Determine the new owner of the record. The options are:
- Logged-In User - The user who is running the application when the rule is triggered. (Not the designer who created the rule.)
- Note: This value is undefined for a record that is created or updated by a Process.
- Pick a User - A lookup field appears. Use it to select a specific user.
- Select a User Field - The [Choose User] button appears. Use it to select a Lookup field that targets the Users object.
- That field can be defined in the current record or in the record the Lookup points to, up to 5 levels deep.
- For example: Owner > Reports To > Reports To_id assigns the record to the current owner's second-level manager.
- Use an expression - Use a combination of fields and expression operators to choose the user to assign to.
- This feature is commonly used to specify if-then logic, or to find a User field defined in an associated record.
- For example, for Case with a Lookup to an OrderItem, the Rule might choose OrderItem > Order > Customer > Agent in Charge_id
- That setting would assign the case to the "troubleshooter" who handles issues raised by that customer.
Assign to Team
- Determine the group the record goes to, so members of the group can claim it.
Send Email
- Send a message, optionally using an Email Template
- Note:
Do not choose a template that includes a JSP page as an attachment.
Learn more: JSP Attachment DeprecationStart Process
- Automatically initiate a Process.
Note: One you start a process, you cannot stop it half way and resume it from that point at a later time. A process always restarts from the first step.
Invoke IS Service
Select this to communicate with Integration Server (IS). It allows you to fetch a list of all the IS packages that you created in the Software AG Designer for the runtime application. You can view all the services that are part of each IS package. Designer is a separate application and is available to you as part of the Integration Server package. For more information about this action, see Invoking Integration Server Services from Business Rules.
Create Task
- Create a new task and specify its settings:
- Owner - Who should perform the task.
- Subject - Title of the task.
- Duration - How long it is expected to take.
- Do not notify - A notification is sent automatically, unless this box is checked.
- Description - Description of the activity to perform.
Use the Record Variable selector to add references to record fields, dates, times, user data, and company information.Change Process Status
- Set the status of the process.
- Change process shows the following statuses:
- Enable: You can enable the process instance, only if the current process status is DISABLED.
- Disable: You can disable the process instance, only if the current process status is READY. You cannot disable a process which is currently in progress state.
- Stop: You can stop the process instance, only if the current process status is STARTED.
Execute Rule Set
- Chain to a different Rule Set, and execute those Rules. Come back to this set when done, and resume processing with the next Rule.
Invoke Method
- Learn more: Invoke a method in a Java Class
Execute Web Service
- Select a Web Service, and specify the mappings for its input and output parameters.
Return Process Decision Value
- This action can be taken by a Rule in a Rule Set whose return type is "Process Decision Value".
- The specified value becomes available for testing in a Process Decision Switch.
- When this action is taken, rule processing stops.
- Learn more: Rule Set Properties
Return Step Owner
- This action can be taken by a Rule in a Rule Set whose return type is "Step Owner".
- Select the User or Role, who will be assigned the task associated with a Process step.
- When this action is taken, rule processing stops.
- Learn more: Rule Set Properties