Difference between revisions of "Exercise 04: Creating Forms"
From AgileApps Support Wiki
Wikieditor (talk | contribs) |
Wikieditor (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 117: | Line 117: | ||
:* When a User types data into a Form field | :* When a User types data into a Form field | ||
:** You can ensure that the data enter is valid | :** You can ensure that the data enter is valid | ||
:** Example: a ZIP code has the correct number of | :** Example: a ZIP code has the correct number of digits | ||
:* Create Validation Expressions | :* Create Validation Expressions | ||
:** Common functions: IF, DATECOMP (compare), TODAY, NOW | :** Common functions: IF, DATECOMP (compare), TODAY, NOW | ||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
:*** Always [Check Syntax] | :*** Always [Check Syntax] | ||
:** Specify the error message to display to the user if the data is not valid | :** Specify the error message to display to the user if the data is not valid | ||
<br><br>[[File:Form_Validation.png|600px]]<br><br>[[File:Form_Validation_01.png| | <br><br>[[File:Form_Validation.png|600px]]<br><br>[[File:Form_Validation_01.png|800px]]<br><br> | ||
===Custom Form Actions=== | ===Custom Form Actions=== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:06, 16 December 2022
Introduction
Forms
- A Form is the user interface for an Object
- Defines what is displayed when a user views or edits a record
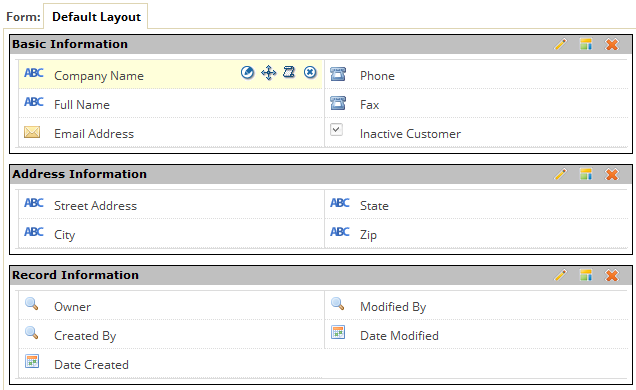
- Every Object gets an automatically-generated default form (Default Layout)
- You can build other Forms to show data to different User Roles
- A Form is the user interface for an Object
Creating a Form
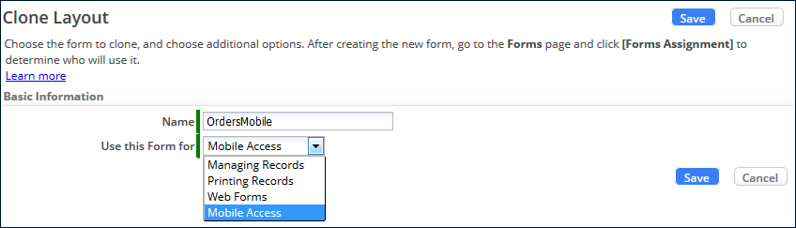
- Specify what to use the Form for:
- Managing Records
- Printing Records
- Mobile Access
- Web Forms
- Specify what to use the Form for:
- Specify other options:
- Properties
- Show field hints
- Display in sidebar: Actions-list, print action, Tasks, files/attachments, Processes, …
- Form Scripts
- On Load and On Save processing using JavaScript
- Common functions used for both events can be defined
- Layout Rules
- Dynamically vary what is displayed and what is required, based on conditional expressions
- Properties
- Specify other options:
Editing Form Layout
- WYSIWYG editor allows you to design the UI as it looks
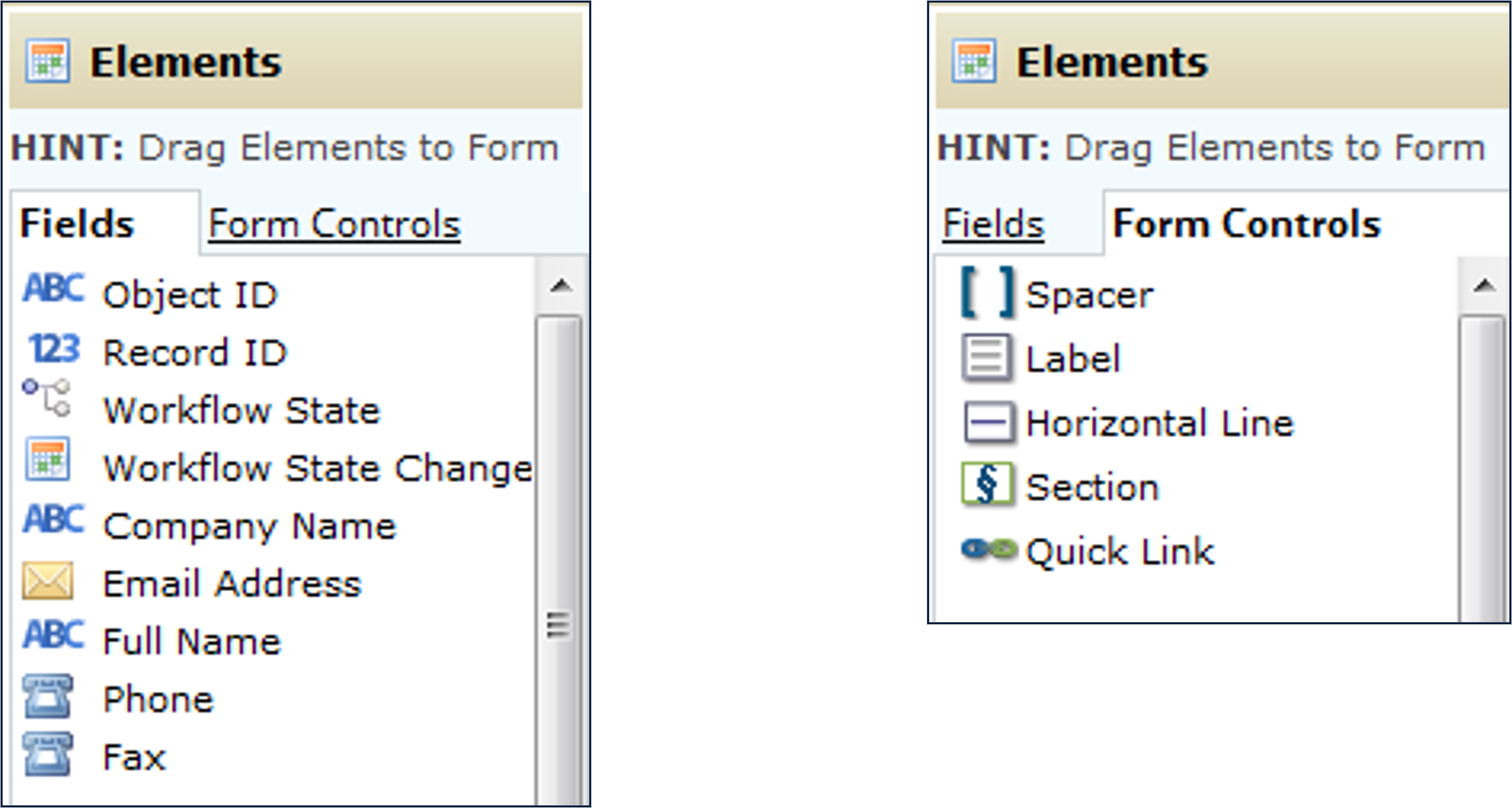
- Forms have Field Elements (fields) and Form Controls (form spacers and sections used to structure the form)
- Drag and drop Fields and Form Controls from the palettes to any section in the Form
Form Fields
- To modify a Field in a Form, click one of the Field’s icons:
- Edit Field
- Move Field
- Field Script
- Remove Field
- To modify a Field in a Form, click one of the Field’s icons:
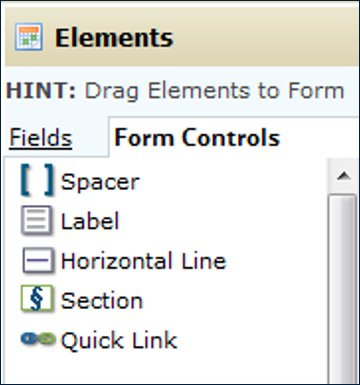
Form Controls
- Spacer
- Vertical space between elements in a Form
- Commonly used in a multi-column form where one cell is blank�
- Label
- Horizontal Line
- Adds a divider between elements in a section�
- Section
- A way to break one form into parts that will be displayed using separate tabs�
- Quick Link
- Provides the ability to pass a value from a record to a website URL
- Spacer
Related Information Section
- Recap:
- Objects can be related via Object Relationships
- “Detail” Objects have (generated) Lookup fields �to their “Master” Object�
- Related Information section of a Form displays records of related Objects
- Records of other Objects that contain a Lookup to the current record
- Automatically created for all related Objects
- Can be customized
- Recap:
- Example:
- When viewing a Customer, the Related Information section shows you all Orders the Customer has made
- That view is made possible by the fact that the Orders Object has a Lookup to Customers
- Example:
Rollup Summary Fields
- Rollup Summary Fields summarize information contained in related records that have a Lookup to the current Object
- Rollup Summary Field can be used to get a Record Count, Sum, Average, Maximum, or Minimum value from related records
- The Lookup field that targets the current Object must be the first field in an Index defined on the detail Object
- Rollup Summary Fields are calculated asynchronously in the background by default
- Rollup Summary Fields:
- are universal, read-only fields
- should not be used to build filter criteria for Formulas, Data Policies, Validations, Indexes, or Searches.
- cannot be created based on another Rollup Summary Field
- can be created only in Master-record Objects
Mobile Access Forms
- The AgileApps interface is mobile-enabled, right out of the box
- All interaction with Forms and other platform operations can be accomplished using a mobile device�
- You can also define Forms specifically for mobile use
- The AgileApps interface is mobile-enabled, right out of the box
- Also:
- Clicking on a Geolocation Field automatically fills in the user’s location
- Clicking on an Image Field automatically activates the camera
- Also:
Web Forms
- Allows external customers to create new Object records
- Two types of Web Forms:�
a) Linked Form (also known as a "Case Form Link")
- Clone an existing Form (such as the Default Layout)
- Specify “Use this Form for” = Web Forms
- Add the From Name and From Address fields to the Form, make them required
- Create a Web Form of type “Case Form Link”
- Choose a Form from a list of Forms that have been previously created on the platform
- Choose to accept email from anyone or existing contacts only
- Fields to include are chosen when you design the assigned Form
- Web Form is hosted by the AgileApps platform -> copy & paste the link to your external page
- Platform does error processing and messaging
- HTML formatting and the [Submit] button label are fixed
- Clone an existing Form (such as the Default Layout)
b) Customizable HTML (also known as "Generated HTML")
- Create a Web Form of type “Customizable HTML“
- Specify which fields to include in the form, arrange them, and specify which are required
- Choose to accept email from anyone or existing contacts only
- Copy the generated HTML into your page, customizing it in whatever manner you want
- An HTML version of the Form is generated, with a [Submit] button
- The HTML and button name can be fully customized
- You must implement error handling on your own
- Create a Web Form of type “Customizable HTML“
Assigning Forms to Application Roles
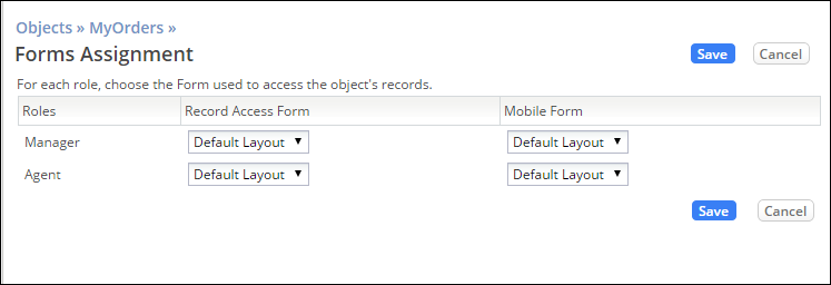
After you create a Form:
- For each Application Role defined in the application:
- Select the Form used to access the current Object's data
- Make one selection for online access and one for mobile access
- For each Application Role defined in the application:
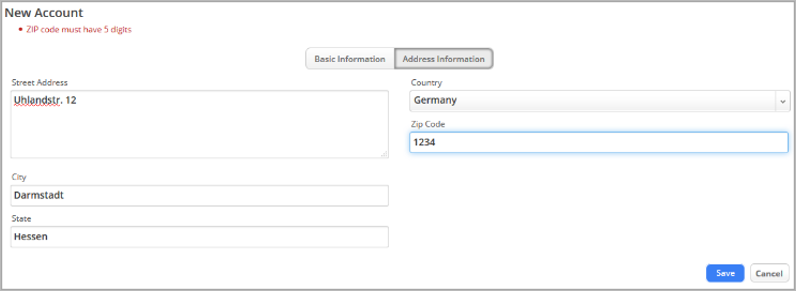
Validating Data in a Form
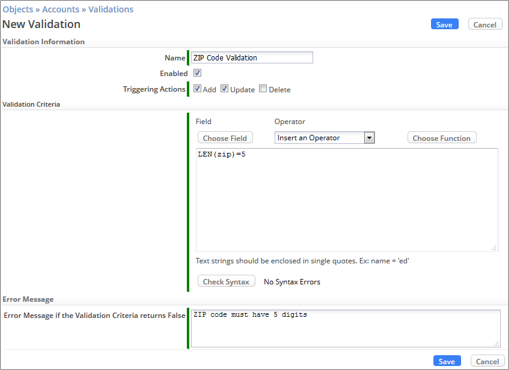
- When a User types data into a Form field
- You can ensure that the data enter is valid
- Example: a ZIP code has the correct number of digits
- Create Validation Expressions
- Common functions: IF, DATECOMP (compare), TODAY, NOW
- You can write expressions that are true when data is NOT valid
- Write an expression for valid data, and surround it with: !(…)
- Always [Check Syntax]
- Specify the error message to display to the user if the data is not valid
- When a User types data into a Form field
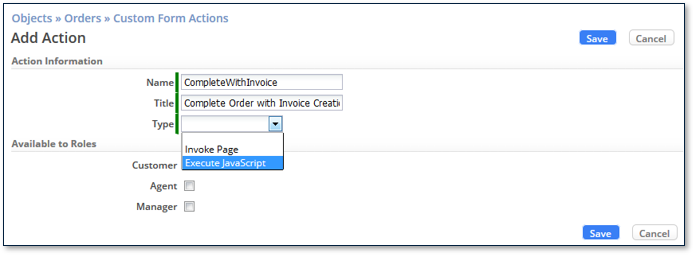
Custom Form Actions
- For a User, Custom Form Actions appear in the sidebar in the Actions dropdown list
- You can configure Custom Form Actions to invoke:
- JavaScript
- A Page which is a standard JSP (Java Server Page)
- For more complex actions use Macros (see later)
- Make the Action visible to Application Roles
- Example:
- Create an invoice record when finishing a Case
Executing JavaScript in AgileApps Cloud
- Forms: “On Load” and “On Save” events (plus shared functions)
- Fields: “On Focus” and “On Change” events (plus shared functions)
- Custom Form Action: Action implementation
- Lookup Fields: Post Selection JavaScript
- JSP/HTML Page: Client-side processing without affecting the Agile Apps platform
Use to:
- Access data in Form fields
- Manipulate fields (validate, hide, make visible, make required)
- Execute platform REST APIs
- Access remote servers
- Add buttons
- Open a platform JSP page or external HTML page
Resources
Exercise
In webMethods AgileApps Cloud, a Form defines the fields that are visible to a User when the User views or edits an Object record. This exercise has four parts:
- In Part 1, you update the Default Layout Form.
- In Part 2, you validate data in a Form field.
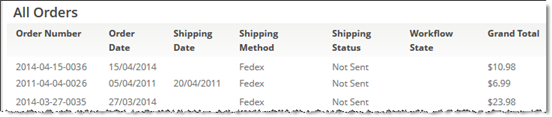
- In Part 3, you add new fields to your Objects, and update them in the Form.
- In Part 4, you create a new Form and assign it to an Application Role.
- In Part 5, you learn how to create a Web Form for Orders for use on an external site.