Difference between revisions of "Cascade Rules and Aliases"
From AgileApps Support Wiki
imported>Aeric m (Text replace - 'Designer > Objects' to 'File:GearIcon.png > Customization > Objects') |
imported>Aeric |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The ''cascade rules'' specify which operations are allowed when using the [[Composite Object]] APIs. The [[#Cascade Delete Rule|Cascade Delete Rule]] also triggers an auto-delete of detail records in a [[Master-Detail relationship]]. | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
===About Cascade Rules and Aliases=== | ===About Cascade Rules and Aliases=== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
Cascade rules restrict or allow add, update and delete access to related objects. They determine which operations are allowed on subsidiary objects in a composite relationship. | Cascade rules restrict or allow add, update and delete access to related objects. They determine which operations are allowed on subsidiary objects in a composite relationship. | ||
The following choices are available: | ====Available Rules=== | ||
The choices you can make depend on the type of relationship. The following choices are available: | |||
:{| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" | :{| border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" | ||
!Relationship Type | !Relationship Type | ||
| Line 53: | Line 54: | ||
| Many to One ||Any Object ||Any Object || -- ||align="center"|[[File:Checkmark.gif|link=]] || -- || -- | | Many to One ||Any Object ||Any Object || -- ||align="center"|[[File:Checkmark.gif|link=]] || -- || -- | ||
|} | |} | ||
====Cascade Delete Rule==== | |||
The Case Delete Rule has a dual purpose: | |||
:* When the "master" record in a one-to-many relationship is deleted, "detail" records are deleted automatically. | |||
::''Learn more:'' [[Master-Detail relationship]] | |||
:* When the [[Composite Object]] APIs are used to update a master record, detail records can be deleted at the same time. | |||
===Specifying Aliases and Cascade Rules=== | ===Specifying Aliases and Cascade Rules=== | ||
Revision as of 19:41, 30 July 2014
The cascade rules specify which operations are allowed when using the Composite Object APIs. The Cascade Delete Rule also triggers an auto-delete of detail records in a Master-Detail relationship.
About Cascade Rules and Aliases
- Cascade rules are established by the application designer. They determine which operations are allowed on dependent objects in a relationship.
- The alias gives the relationship a name. In the data stream passed to the composite request handler, the alias is a wrapper for the dependent records in a relationship. The resulting structure looks like this:
- <syntaxhighlight lang="xml" enclose="div">
primary record
|...primary record data... |relationship alias for secondary object | secondary record #1 | |...secondary record data... | |relationship alias for tertiary object | | tertiary record #1 | | |...tertiary record data... | | |... | |... | secondary record #2 |...
</syntaxhighlight>
- Notes:
- Relationships can nest to arbitrary depth.
- Relationship aliases will generally have the same name as the dependent object.
Cascade Rules
Cascade rules restrict or allow add, update and delete access to related objects. They determine which operations are allowed on subsidiary objects in a composite relationship.
=Available Rules
The choices you can make depend on the type of relationship. The following choices are available:
Relationship Type Foreign Object Id Junction Foreign Object Id Add Update Delete Orphan Delete One to Many Other than User -- 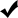
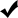
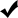
-- One To Many User -- -- 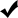
-- -- Many to Many Any Object Other than User 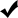
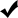
-- 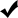
Many to Many Any Object User -- 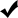
-- -- Many to One Any Object Any Object -- 
-- --
Cascade Delete Rule
The Case Delete Rule has a dual purpose:
- When the "master" record in a one-to-many relationship is deleted, "detail" records are deleted automatically.
- Learn more: Master-Detail relationship
- When the Composite Object APIs are used to update a master record, detail records can be deleted at the same time.
Specifying Aliases and Cascade Rules
Prerequisites:
- All objects and junction tables have been created.
- Lookup fields have been defined in the objects to establish the relationships
To specify aliases and cascade rules:
 > Customization > Objects
> Customization > Objects- Select the primary object in the relationship.
For example, if Order_Items has a Lookup to Orders, then Orders is the primary object, and Order_Items is the dependent object. - In the Properties tab, scroll down to Related Information
A list of dependent objects appears. So if Order_Items has a Lookup to Orders, then Order_Items appears in the list. (The Users object always appears twice: for the creator of the object, and for the most recent person to modify the object.) - Select the object relationship you want to specify.
For example, select the Order_Items object. The Manage Object Relationship window appears. - Specify the type of relationship: Either One-to-Many or Junction if this is a junction object for a Many-to-Many relationship.
If you select many-to-many:- The 'Select Foreign Object field lists the targets of the other Lookup fields in the junction object.
(Typically there will only be one, but there could be more.) - From that drop down, select the secondary object in the Many-to-Many relationship
The next drop down is then automatically populated with the lookup field.
- The 'Select Foreign Object field lists the targets of the other Lookup fields in the junction object.
- Specify the name of the relationship alias.
Typically, that will be a lowercase, plural version of the dependent object's name, but you may need different aliases if the same object is used in multiple dependent relationships. For example, in the Order object, the alias for the Order_Item object might typically be specified as items. - Specify the cascade rules. Depending on the type of relationship you have defined, you can enable the capability to:
- Add dependent records
- Update dependent records
- Delete dependent records in a one-to-many relationship
- Do an "orphan delete" for a many-to-many relationship
(Automatically delete the dependent record if no more records point to it.)